NSAIDs and the Tinnitus Puzzle: Unraveling the Hidden Link
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Are you frequently reaching out for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage your pains and aches? Did you ever notice a constant buzzing or ringing sound in your ears afterward? If your answer is yes, you might be experiencing a condition known as Tinnitus. Hence, let’s delve into this topic and understand whether NSAIDs can cause Tinnitus or not.
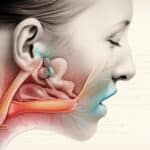
Tinnitus Definition, Prevalence, and Symptoms
Ever heard a faint buzzing or a high-pitched whistling sound when it’s all quiet? You may be experiencing what’s known as Tinnitus. It’s an internal sound often described as a ringing, buzzing, humming, or whistling. It may be continuous or periodic, and it’s often more noticeable in a quiet environment. According to the Omegax Research Foundation, it affects about 15-20% of people.
Tinnitus can be subjective – perceived only by you, or objective – heard by others. Symptoms include hearing sounds when no sound is present and the sounds could vary – from ringing and buzzing to hissing and clicking. But can NSAIDs cause it?
Understanding NSAIDs – Their Common Examples and Uses
NSAIDs, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are a broad category of medications commonly used to reduce pain, inflammation, and fever. Examples of NSAIDs include common over-the-counter drugs like ibuprofen and aspirin, as well as more potent prescription medications such as Naproxen and Diclofenac. NSAIDs are frequently prescribed for arthritis, muscle injuries, and other inflammatory conditions.
Common Uses of NSAIDs and Their Side Effects
These drugs work by blocking enzymes that produce prostaglandins, the substances responsible for inflammation and pain. While NSAIDs can be hugely beneficial, they’re not without potential side effects. According to Effexor and Tinnitus, common adverse effects may include an upset stomach, heartburn, and ulcers. But an often overlooked potential side effect is Tinnitus.
Though research is ongoing to substantiate this claim, some studies suggest a relationship between NSAID use and Tinnitus. So, before taking any medication, consider the pros and cons, and more importantly, consult a healthcare provider.
Why do NSAIDs Cause Tinnitus? – The Crucial Link
It’s observed that NSAIDs can potentially impair the blood flow to the cochlea – an essential part of the inner ear that converts sound waves into nerve signals, leading to Tinnitus. With the hampered blood flow, the nerve cells may be deprived of essential nutrients, causing ‘phantom noises.’ This is a theory trying to explain the connection between NSAIDs and Tinnitus. However, the whole scenario is not crystal clear, and more research and studies are to be done to establish a firm link.
Comprehensive Review of Relevant Studies on NSAIDs and Tinnitus
When embarking on the quest to decipher the relationship between NSAIDs and Tinnitus, we stumble upon various research papers and studies. One study from the American Journal of Medicine revealed that regular and extended use of aspirin, a frequently used NSAID, could lead to Tinnitus.
Further, another research report on PubMed reflected that about 1% to 3% of NSAID users experienced Tinnitus. These studies hint at the possibility of a connection between Tinnitus and NSAIDs, yet the direct cause-effect relation remains a puzzle.
A Case Study Focusing on NSAID-Induced Tinnitus
In an intriguing case study cited by Prozac and Tinnitus, a patient experienced Tinnitus after consuming Ibuprofen for a couple of weeks to ease muscle discomfort. Upon discontinuation of the drugs, the symptoms of Tinnitus markedly receded within a week.
NSAIDs and Tinnitus – Is it Reversible?
So, we come to the million-dollar question – If NSAIDs cause Tinnitus, is the condition reversible post-NSAID cessation?
From some anecdotal evidence and case studies, it seems that Tinnitus symptoms could potentially reduce or even disappear after stopping the consumption of NSAIDs. However, this may vary from one person to another, depending on numerous factors like overall health status, the severity of the symptoms, and individual drug tolerance.
Remember, if you find yourself experiencing Tinnitus after taking NSAIDs, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide the necessary guidance and discuss other viable pain management options, limiting the risks of Tinnitus.
Alternatives to NSAIDs – Managing the Risk of Tinnitus
It’s essential to consult your healthcare provider when Tinnitus symptoms manifest, and you suspect NSAIDs as the possible culprit. Other pain management options may be safer for those risking Tinnitus due to NSAID usage. For instance, Betahistine for Tinnitus has shown promising results. Similarly, Melatonin is another alternative found helpful by many Tinnitus sufferers. Such alternatives could potentially offer relief without the threatening side effects of Tinnitus.
Key Takeaways on NSAIDs and Tinnitus
To wrap things up, though NSAIDs can be effective in treating pain and inflammation, they may cause Tinnitus in some individuals. Understanding these risks and knowing your alternatives can help manage unwanted side effects like Tinnitus better. Moreover, as with all medication, it’s crucial to follow the guideline – “Start low, go slow.”
Conclusion
All in all, it’s critical to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect Tinnitus symptoms after consuming NSAIDs. Remember, each person is unique, and so is their reaction to different classes of drugs. Prevention and prompt treatment often ripple down to staying well-informed, linking the dots, and of course, your active involvement in managing your health! As put perfectly by Effexor and Tinnitus, a stitch in time saves nine!
While the potential link between NSAIDs and Tinnitus could feel daunting, let’s not lose sight of the fact that health sciences and medicines have come a long way. We are slowly, but surely, unfolding the roots of health conditions and delivering meaningful solutions. Here’s to hoping for a future where we have our cake and eat it too – No pain, no Tinnitus!
On that note, always feel free to deep-dive and understand more about Tinnitus and its myriad facets here. Knowledge, indeed, is power. So, arm yourself and take charge!
Can NSAIDS Cause Tinnitus - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
While the link between NSAIDs and Tinnitus is not yet definitively established, some scientific evidence and user experiences suggest a potential connection. It’s always advisable to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect Tinnitus symptoms after consuming NSAIDs.
Common signs include hearing sounds like ringing, buzzing, humming, or whistling when no external sound is present. These sounds could be periodic or continuous and are often more noticeable in a quiet environment.
Though anecdotal evidence suggests Tinnitus symptoms may reduce or disappear after stopping the consumption of NSAIDs, the effect can vary from person to person. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider if you experience Tinnitus after taking NSAIDs.
Yes, there are alternatives to NSAIDs that may bring relief from pain and inflammation without the risk of Tinnitus. These include substances like Betahistine or Melatonin that have shown promising results for Tinnitus sufferers.
“For more detailed and up-to-date information, consider navigating through various sections of Pulsatile Tinnitus Treatments , a comprehensive platform dedicated to understanding, managing, and treating Tinnitus.
The post NSAIDs and the Tinnitus Puzzle: Unraveling the Hidden Link appeared first on Pulsatile Tinnitus Treatments News - Tinnitus Relief.
Related posts:
https://ift.tt/NjrXCu8
#tinnitus #pusatiletinnitus #earringing #whatistinnitus #howtostoptinnitus
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps


Comments
Post a Comment